
Publishing
Introduction
To publish an HTML document, you need to transfer a copy of it on a remote computer, called server.You can think to a server as a warehouse-distributor. His service is called hosting.
An hosting service may be provided whether for free or not.
There are thousands of them; to find and subscribe to an hosting service, you will probably follow these steps:
- use a search engine to find one, typing for example "web hosting" or "web space" or "free web space"
- read the service's features and approve his terms of use;
- register, giving some personal data (generally, a valid email address is required);
- note what username and password are assigned to your account;
- note your http address and, if provided, your ftp address, which use is described
further.
There are two ways to put (upload) or get (download) and manage (rename, move, delete) files and directories on the server: using the browser, or using an FTP client.
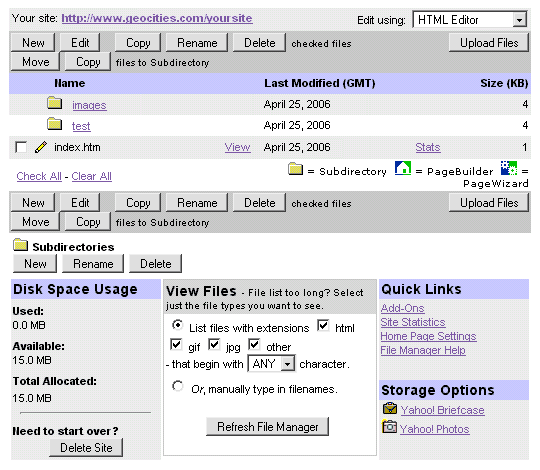
This screenshot shows the typical Geocities file manager.
It's not a program, but a password protected web page that you use simply trough your browser.
This is a screenshot of a simple FTP client, showing some files placed on a site.
The most of the FTP clients have an interface similar to this, analogous to Windows Explorer.
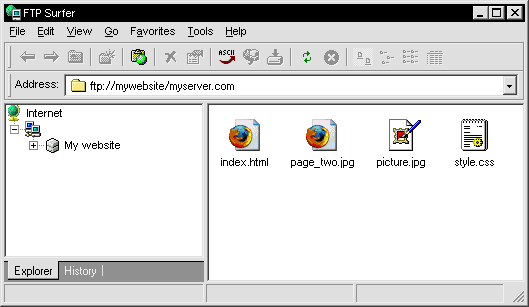
An FTP client is, generally, faster and more practical than a browser-based file manager.
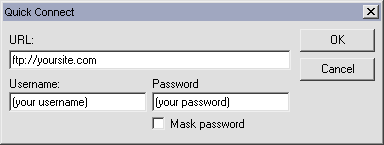
To connect to your server, you need to enter FTP address, username and password.
Usually, these informations can be saved as configurations options, so you don't need to provide them every time.
- ASCII, for plain text files:
txt, htm, html, css, xml files, and those which are readable with a plain text editor; - binary, for binary files:
jpg, gif, png, doc, pdf, zip, exe files, and those which are not readable with a plain text editor.
Home page and directories
The home page is the essential document of the web site: the address of the site is also the address of the home page.The home page must be a single HTML file named index.html or index.htm, and must be placed in the main directory of the site, also called root directory.
All other pages, images and files can be placed whether in the root directory or in subdirectories.
For example:
suppose to upload the home page "index.htm", a page called "credits.htm" and an image called "apple.jpg" in the main directory of our site, which address is http://www.mywebsite.com.
Their correspondent addresses will be:
http://www.mywebsite.com/index.htm http://www.mywebsite.com/credits.htm http://www.mywebsite.com/apple.jpgThen, imagine to put "credits.htm" in a subdirectory called "docs" and "apple.jpg" in a subdirectory called "images".
Their addresses change correspondently:
http://www.mywebsite.com/index.htm http://www.mywebsite.com/docs/credits.htm http://www.mywebsite.com/images/apple.jpgNote: "index.htm" can't be placed elsewhere, it remains in the main directory.
Hence, his address is always the same:
http://www.mywebsite.com
or
http://www.mywebsite.com/index.htm
Next page :
how to ...